This is a comprehensive guide to Super Absorbent polymers. Learn what super absorbent polymers are, how they are made, what they can do, applications and get answers to many of your questions.
OVERVIEW
Super absorbent polymer, also referred to as SAP or superabsorbent material SAM, is used in a broad range of applications for both consumer and industrial markets due to their incredible affinity for water and aqueous based solutions, typically absorbing up to 500 times their own weight of liquid. Superabsorbent polymers were first developed in the 1960’s by the US Department of Agriculture as part of a project to improve water conservation in soil. This initial polymer was based on acrylonitrile polymer attached to starch molecules. However, over time the chemistry advanced and the use of starch-based polymers diminished and more modern SAP technology using hydrocarbon derived polymers were developed based on crosslinked acrylic polymers neutralized with sodium.
These new superabsorbent polymers were subsequently found to be very effective in disposable personal hygiene products in addition to agriculture, and this led to their first use in sanitary napkins in 1978 and baby diapers in 1982. Since those early days, superabsorbent polymers have grown into a hygiene industry staple with circa 3 million tons being produced annually, predominantly for use in feminine hygiene pads, baby and adult diapers plus other incontinence products.
SUPERABSORBENT CHEMISRTY
Formation of Superabsorbent polymers
Superabsorbent polymers used in Gelok laminates and airlaids are typically made from the reaction of acrylic acid monomer with sodium hydroxide and a cross-linking agent, forming a polyacrylic acid sodium salt. Cross-linking agents such as Tetraallyl ethoxy ethane and ‘TMPTA’ are critical to this process as they form the bond between the polymer chains. There are three techniques used to produce the superabsorbent polymers.
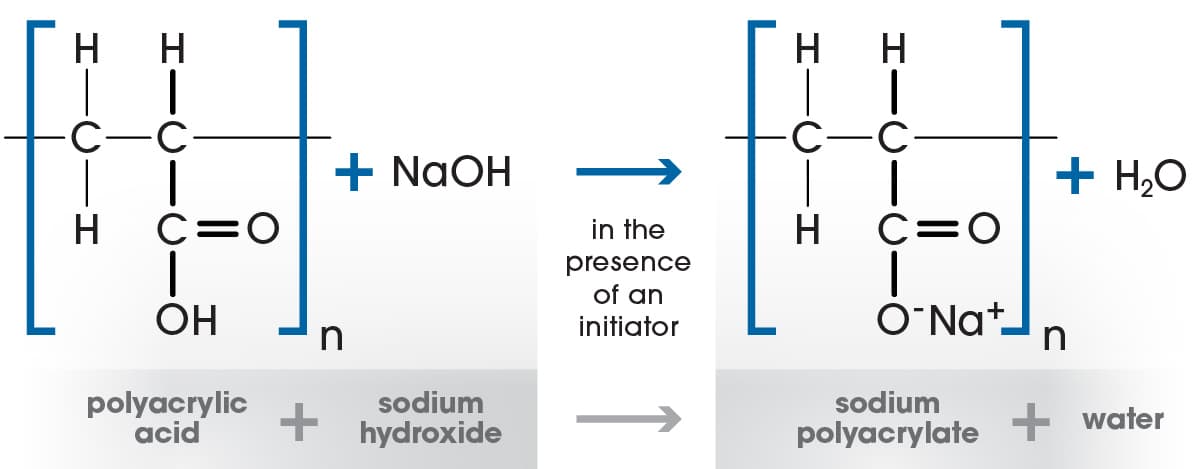
Gel Polymerization
The most common technique is a process called ‘Gel Polymerization’ wherein acrylic acid, sodium hydroxide, water, cross linking agents and UV initiators are all sprayed onto a moving belt inside a long chamber with a row of high intensity UV lights. The UV radiation forces the components to react on the belt and crosslink, thereby forming the sodium polyacrylate. The mixture swells up in the chamber into a ‘wet cake’ which is passed into a mill to be ground up and then conveyed to drying equipment. The dried superabsorbent granules can be further treated with additional ‘surface’ cross-linking agents to improve performance characteristics such as absorption capacity, rate of acquisition and permeability.
Suspension Polymerization
An alternative manufacturing technique is ‘Suspension Polymerization’. In this method the key ingredients; typically sodium hydroxide, acrylic acid, initiators, crosslinking agents and a surfactant are suspended in a tank reactor in an organic solvent. The acrylic monomer is insoluble in the solvent and reacts with the base to form cross-linked sodium polyacrylate polymer beads. The size of the polymeric beads is determined by close control of temperature, residence time, speed and type of agitator in the reactor as well as the concentration of the multiple additives. The emulsion is continuously drawn from the reactor and the spheres are filtered out of solution, agglomerated and dried. The organic solvent is recycled into the reactor. The dried superabsorbent polymer can be further processed at this stage with ‘surface cross-linking’ initiators to enhance critical performance factors. The SAP is then dried again and bulk packaged as required.
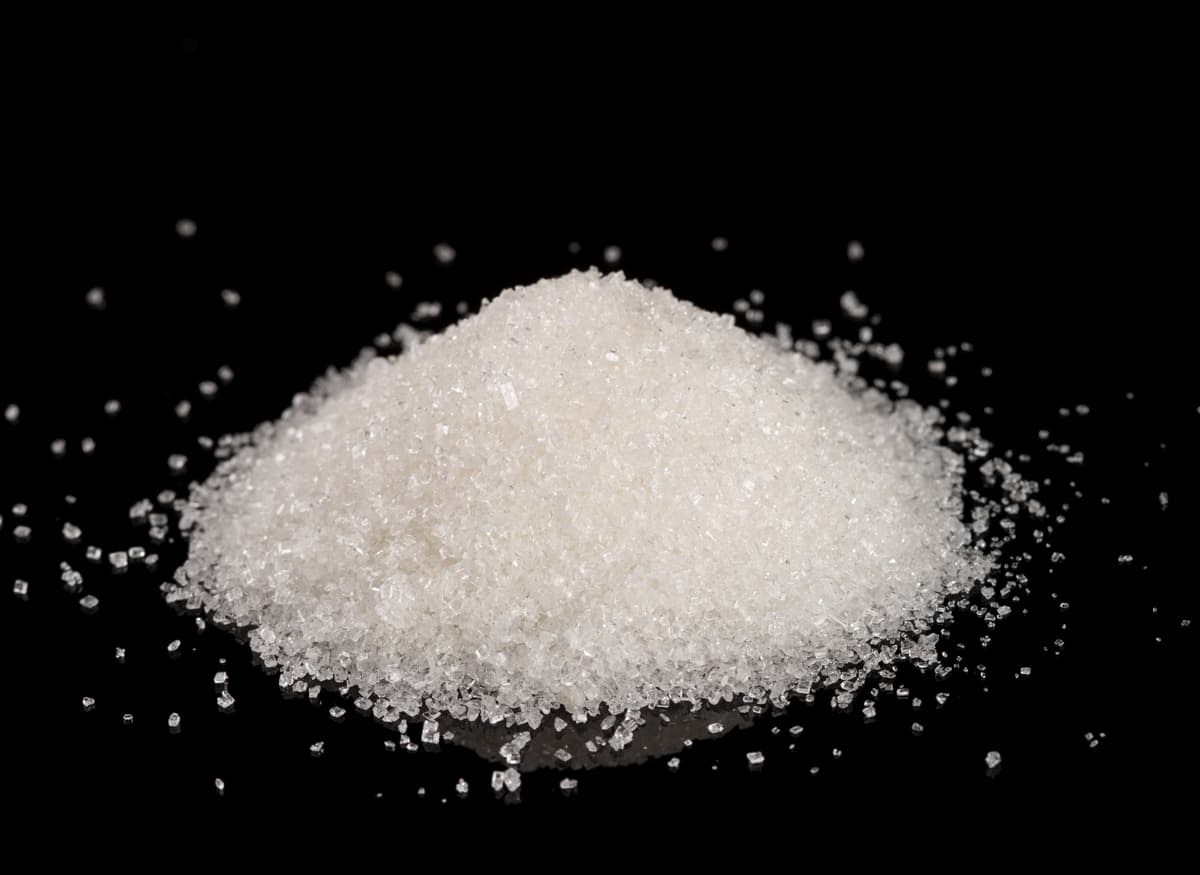

Superabsorbent particles [-CH2-CH(CO2Na)-]n
Solution Polymerization
A third common manufacturing process is called ‘Solution Polymerization’. The acrylic acid monomer is dissolved in a non-reactive solvent along with an initiator, sodium hydroxide and crosslinking agents. The reaction results in a polymer that is also soluble in the solvent. By careful control of the temperature and concentration of ingredients the desired degree of conversion can be achieved, without the bulk polymerization as in suspension polymerization. The excess solvent is removed and the ‘liquid superabsorbent polymers’ are ready for application. Typically for non-woven markets the polymeric solution would be applied to cellulose fibers, then the solvent is dried off leaving a superabsorbent coated fiber.
Application of superabsorbent polymers
When the sodium polyacrylate superabsorbent polymers come in contact with aqueous liquids such as urine, blood or exudate the polymer absorbs the water through the process of osmosis i.e., the superabsorbent particles act like semipermeable membranes, absorbing the water molecules and swelling considerably. In fact, one gram of superabsorbent can absorb several hundred grams of pure water and retain extremely large amounts of that water even under moderate pressure. Hence why these superabsorbers are so ideally suited for personal hygiene and incontinence applications as diapers and pads can be exposed to appreciable amounts of ‘body pressure’ whilst sitting or laying down.
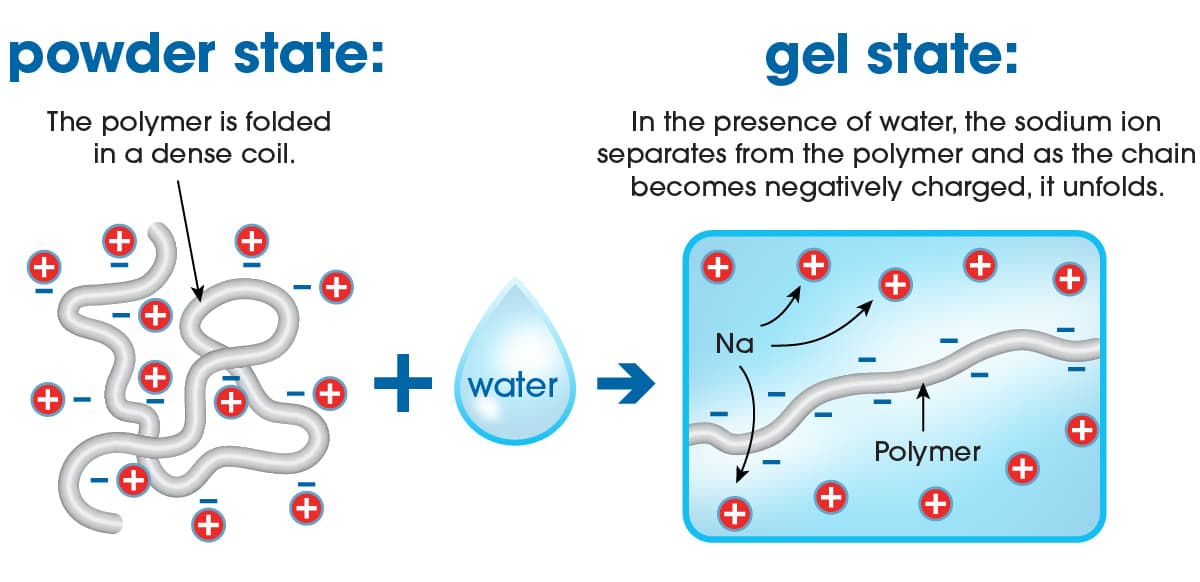
Superabsorbent polymer absorbing water
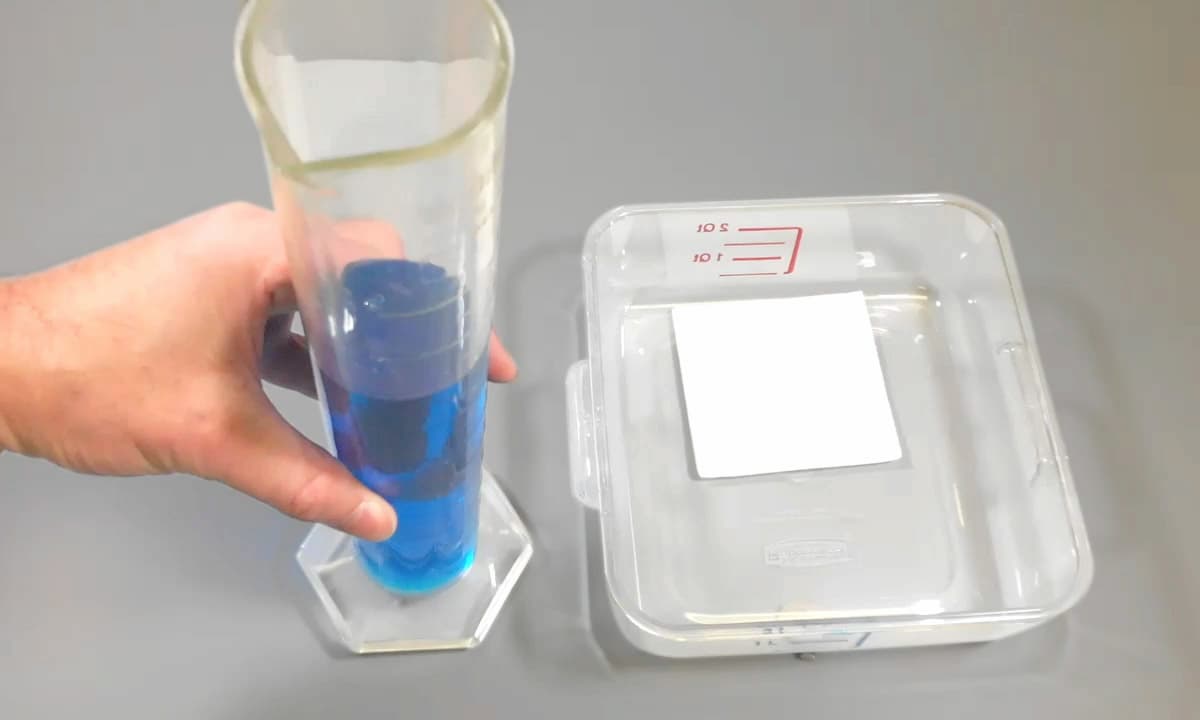
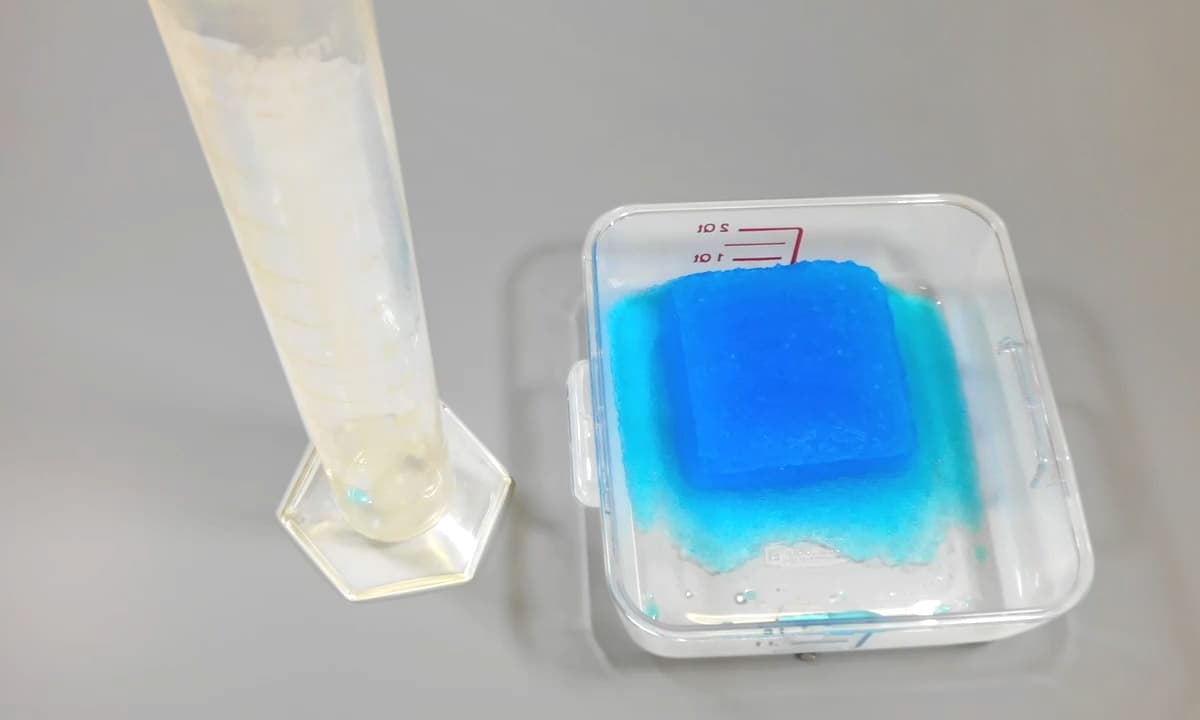


However, when sodium polyacrylate is in contact with aqueous liquids containing high levels of salts such as urine, exudate, or blood, then the osmotic effect is impeded and will lower absorbent capacity to just tens of grams of the ‘salty’ liquid.
The superabsorbent polymer’s liquid absorption and capacity characteristics can be controlled by the type and quantity of cross-linking agent and used to produce different saps. Low density SAP’s typically have a higher absorbent capacity in terms of gram for gram absorbency, whereas highly cross linked SAP’s will have a lower capacity but greater gel strength and increased ability to retain liquid under pressure. Other characteristics such as speed of absorption, liquid permeability or deodorization capability can be similarly manipulated.
IMPORTANT CHARACTERISTICS OF SUPERABSORBENT POLYMERS
- Particle size
- Free swell absorption capacity (water content)
- Absorption capacity under load (water content under pressure)
- Water retention properties
- Rate of water absorption
- Polymer permeability
- Gel strength
- Wicking capability
MAJOR MANUFACTURERS OF SUPERABSORBENT POLYMER WITH ESTIMATED WORLD-WIDE CAPACITY:
- Sumitomo Seika Chemicals (Japan) – 450,000 tons
- Nippon Shokubai (Japan) – 700,000 tons
- Sanyo Chemical / SDP Global (Japan) – 420,000 tons
- BASF (Germany) – 600,000 tons
- Evonik (Germany) – 500,000 tons
- LG Chem (S. Korea) – 400,000 tons
- Taiwan Plastics (Taiwan) – 200,000 tons
- Yixing Danson (China) – 420,000 tons
- Satellite Science & Technology (China) – 200,000 tons
- Shenghong Holding Group (China) – 80,000
- Quan Zhou Technology (China) – 140,000 tons
GELOK APPLICATIONS FOR SUPERABSORBENT POLYMERS
Gelok’s absorbent technology is fundamentally based on the excellent absorptive capability of sodium polyacrylate superabsorbent polymers, i.e., the sodium salt of polyacrylic acid. Products containing super absorbent polymers have a very strong affinity for aqueous based liquids, hence its widespread use in consumer products for personal care, incontinence, wound care, plus a myriad of healthcare and industrial applications where ‘fluid management’ is critical, such as medical packaging or ‘capturing’ biohazard liquids, dewatering of fuel and absorbing industrial wastes.
We have access to a variety of different types of superabsorbent polymers and substrates, thereby enabling Gelok to custom design absorbent cores for customer specific applications. These cores can be either ultra-thin high absorbency ‘laminates’ where the superabsorbent particles are hydrogen bonded between two sheets of tissue, or they can be airlaid-style cores that blend or layer SAP particles with cellulose fibers, also using hydrogen bonding between two layers of tissue.
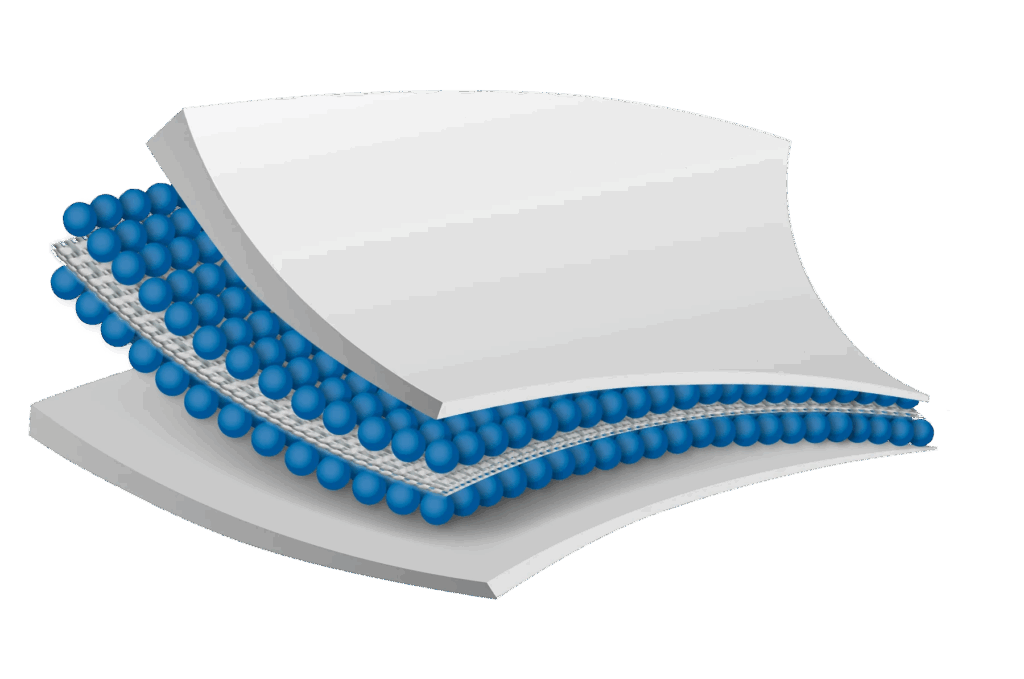
Specialized laminates for water retention can also be manufactured using polyester or airlaid substrates with a blend of superabsorbent materials and adhesive.
All Gelok laminates and airlaid-style cores are produced as bulk rolls that can be slit to customer specified widths or sheeted as required.
All Gelok products are manufactured in a plant whose Quality Management System is certified by Intertek as being in conformity with ISO 9001:2015.
FORMATS FOR APPLICATION OF SUPERABSORBENT POLYMERS
The predominant formats for superabsorbent polymer applications typically fall into one of three categories. These include the use of the polymer in its raw powder form, or the utilization of superabsorbent granules combined with fibers and bonded within cellulose or non-woven laminates, as well as in airlaid structures.
1. The superabsorbent polymer in powder format is generally used for absorbing biological fluids and industrial aqueous fluids, such as spills in medical or commercial facilities, and for specialized usages in funeral homes etc.
2. Cellulose or polyester-based non-woven laminates containing superabsorbent polymer are produced via a relatively simple high pressure laminating process.
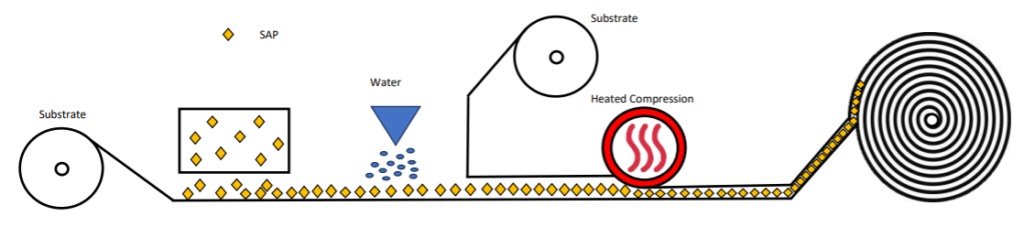
The carrier substrate, be it tissue, airlaid or polyester-type non-woven, moves beneath a dispenser that releases superabsorbent polymers, offering flexibility in polymer weights applied to the carrier. Subsequently, the carrier with superabsorbent polymers pass through a fine water spray to initiate bonding via partial water absorption. The upper substrate is then layered onto the moist superabsorbent polymers and promptly undergoes high-temperature, high-pressure lamination, arresting the absorption process and creating hydrogen bonds.Alternatively, bonding mechanisms like hot melt adhesive or particulate adhesive blended with the superabsorbent polymer, can be employed. These substances melt and disperse throughout the laminate structure during passage through the heated compression zone.Following lamination, the rolls of laminate are securely encased in polyethylene bags due to their hygroscopic nature. Once sealed they can be shipped to the final article manufacturer for further processing.
3. The third and most often used format for superabsorbent polymers is within an airlaid structure.
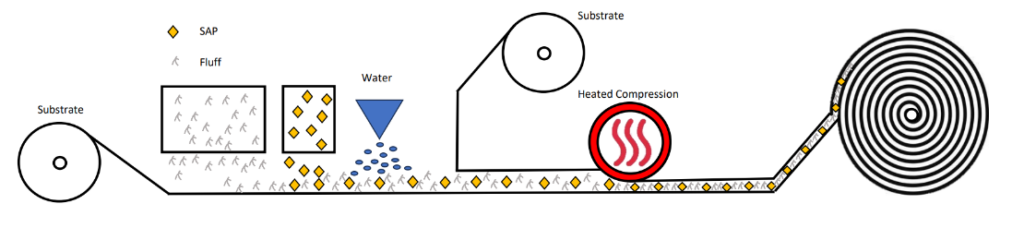
Airlaid cores are available in several formats, including latex bonded, hydrogen bonded, thermal bonded, or multi-bonded. The fundamental process shares similarities with lamination, but airlaid structures involve the deposition of cellulose fibers onto the carrier, along with the incorporation of additives like bicomponent fibers, liquid or particulate adhesives, and alternative substrates. Various airlaid processes may employ multiple formers to deposit distinct layers of fluff and superabsorbent polymers, each with different weights per layer. In comparison to simple tissue-SAP-tissue laminates, airlaid processes and additive options offer a broad range of improved performance and aesthetic or tactile characteristics, such as excellent wicking, stronger bonds, softness, and conformability. This versatility makes them suitable for a diverse array of applications.
COMMON SUPERABSORBENT APPLICATIONS
Meat and fruit pads
Many meat packages in supermarkets now feature absorbent pads at the bottom of a tray to capture escaping juices from the meat. This serves two primary purposes. Firstly, it prevents the leakage of juices onto customers and the supermarket fridge/floor, enhancing cleanliness. Secondly, by effectively absorbing the liquid, these pads help inhibit the proliferation of microbes that could otherwise spoil the meat, contributing to the overall freshness and quality of the product.
Wound dressings
For chronic or acute wounds, such as arterial or venous ulcers, characterized by substantial exudate or blood discharge over an extended duration, specialized dressings incorporating superabsorbent polymers are employed. These dressings possess the ability to absorb and contain the exudate effectively. Due to their high capacity, they can remain in place for extended periods, minimizing the need for frequent dressing changes. This not only enhances patient comfort but also reduces the overall trauma associated with multiple dressing changes.
Medical/surgical pads
Medical pads containing superabsorbent material serve a diverse range of specialized applications within hospitals, laboratories, and other medical facilities. These applications span from pads on operating tables designed to absorb liquids released during surgery to spill pads utilized for mopping up various fluids released by patients on equipment or floors. Additionally, laboratories use pads to contain fluids associated with the testing of biological samples. The versatility of medical pads makes them crucial in maintaining cleanliness, managing fluids, and ensuring a hygienic environment across various healthcare settings.
Personal absorbent hygiene products
Baby diapers.
Adult diapers and disposable absorbent underwear.
‘Booster’ pads that can be situated inside diapers to give increased absorbency and protection.
Underpads – bed pads
Hygiene and incontinence pads.
Biohazard absorption and protection
Superabsorbent polymers, owing to their exceptional absorbency capacity, offer ideal packaging solutions for substances categorized as Category A infectious and Category B/UN3373 biological substances, complying with regulations set by USDOT and IATA ISSG. These regulations establish specific requirements for the type and structure of packaging used for transporting these substances. A crucial element in this packaging is the inclusion of sufficient absorbent products to effectively capture all biological liquids, including urine, blood, fecal matter, and similar fluids. This ensures compliance with regulations while also contributing to the safe and secure transportation of hazardous biological materials.
Environmental protection
Superabsorbent polymers and media play a crucial role in environmental protection, showcasing their utility beyond personal care and industrial applications. The high absorbency capacity of superabsorbent materials makes them valuable components in environmental solutions.
One notable application is the incorporation of superabsorbent materials into “absorbent socks” and hazmat spill kits. These are employed to contain aqueous chemical leaks, preventing the spread of contaminants into the surrounding environment. Additionally, a relatively new application involves using superabsorbent materials in “sand-less, sandbags” available in many DIY retail outlets. These permeable sacks contain superabsorbent materials that rapidly expand upon contact with water. This expansion due to the high water absorption capacity allows them to form a physical barrier, helping to limit potential flood damage from river or sea water. This demonstrates the versatility of superabsorbent polymers in addressing environmental challenges and enhancing protective measures.
Fuel and oil filtration / separation (dewatering)
Superabsorbent polymers exhibit a strong affinity for aqueous liquids but remain inert when it comes to oil-based liquids. This characteristic makes them highly effective in water absorption from various sources, including aviation fuel, gasoline, and diesel, when integrated into fuel filters. The selective absorption properties of superabsorbent polymers contribute to their usefulness in managing and separating contaminating liquids in fuel filtration applications.
Agricultural applications
Agriculture and horticulture use superabsorbent polymer granules to control soil moisture e.g. seed coating, water conservation or enhancement of soil physical properties to increase water retention properties. The agricultural application is particularly important in sandy soil and typically uses potassium polyacrylate based super absorbent polymer which is not harmful to plants and seeds.
Other applications
Artificial snow for movies and theatrical effects is a particularly unique, but very effective application for superabsorbent polymer. By changing the cross linking agent for the polymer the gel polymerization process takes on a distinct behavior. This video provides a fun demonstration of how ‘artificial snow’ is produced using dried superabsorbent granules and tap water.
Instead of forming one solid mass as with gel polymerization the individual dried superabsorbent granules absorbed water and formed agglomerates without bonding to adjacent hydrated granules, thereby creating the appearance of individual fluffy snow flakes. The hydrated structure of the ‘snow flakes’ gives them a moist feel however, they cannot combine to create ‘snow balls’! Over time, the water absorption is reversed through evaporation, causing the granules to revert back to their dried format. This recyclable nature allows them to be reused as needed.
Cement modifiers for civil engineering projects
Underground wire and cable water blocking.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do superabsorbent polymers dissolve in water?
No, the cross-linked polymer chains form a gel with water and do not dissolve.
What affects the absorbency and swelling capacity of Superabsorebent polymers.
There are multiple factors affecting the absorbency of superabsorbent polymers, sucha s
How are superabsorbent polymers used in agriculture?
The superabsorbent material, in the form of potassium polyacrylate, not sodium polyacrylate, can be blended to enhance the performance of soil through improved water retention properties and slow release of a variety of nutrients and water soluble fertilizers. The potassium format is non toxic and hence preferred over sodium-based polymer to prevent salination of the soil which would be detrimental to plants health.
what is superabsorbent polymerS mainly used for
The most prevalent application is in personal absorbent hygiene products such as diapers, sanitary napkins and underpads.
Are SAPs safe for use in Hygiene products?
Yes, Super absorbent polymers are safe for use in personal hygiene products. Their safety is supported by decades of use in a wide variety of hygiene products and the fact that SAPs do not come in direct contact with a wearers skin. In personal hygiene products the superabsorbent powder is encased in a permeable non-woven membrane that allows fluids to pass through but prevents the SAP from escaping and coming into direct skin contact.
What are the advantages of using superabsorbent polymer granules in wound care compared to hydrogels
There are several advantages using sodium polyacrylate powder in wound care – most notably the polymer has a much higher capacity for ‘aqueous fluid’, substantially better wicking performance and capacity under pressure making it superior for acute or chronic exuding wounds.
Are superabsorbent polymers biodegradable?
No, at least none that are produced on a commercially viable scale. However, several research companies are actively working on solutions to improve the biodegradability or compostability of superabsorbent polymers (SAPs), or to develop SAPs derived from renewable resources. This research is driven by the fact that vast quantities of SAPs are discarded as landfill waste every year raising environmental and sustainability concerns.
Why are non-biodegradable SAPs used in hygiene products?
Non-biodegradable SAPs are used for two main reasons, firstly biodegradable alternatives are currently not manufactured on a commercially viable scale, and secondly, SAPs produced from Olefin-derived raw materials offer superior product performance absorbing up to 60g of urine per gram of SAP.
Are superabsorbent polymers harmful?
The polymer itself is not usually an irritation to the skin, but irritation is possible if the manufacturing process results in some residual acrylic acid or monomer. Care should also be take to not inhale the dust or powder nor let the polymer come into contact with eyes or skin.
Is superabsorbent polymer plastic?
Technically, sodium polyacrylate can be considered as a plastic as the polymer chains are derived from hydrocarbon sources.
Can I flush superabsorbent polymer?
No. This is definitely not advised as these water absorbing materials will swell up and retain extremely large amounts of water thereby causing blockages in waste pipes or contaminating sewerage treatment facilities.
Can superabsorbent polymers absorb oil-based Liquids?
No. Superabsorbent Polymers can only absorb aqueous fluids. This is because the primary absorption mechanism is through hydrogen bonding and ionic attraction. Oil molecules are non-polar so they are not attracted to SAPs, unlike water molecules which, being polar, are highly attracted to SAPs.
Can you eat superabsorbent polymer SAP?
Eating superabsorbent material is definitely not recommended as ingestion can lead to the polymer absorbing liquid and swelling up inside the body.
What affects the absorbency and swelling capacity of Superabsorbent polymers?
- Polymer Structure
1.1. Cross-liking density is critical to SAP capacity i.e., if the SAP has a low cross-linked density then it will have a higher capacity but low mechanical properties. Conversely, if there is a high cross-linked density the absorption capacity will be lower, but mechanical strength higher i.e., harder for absorbed liquid to break free.
1.2 A polymer with a greater porosity will have a faster absorption rate and potentially a higher capacity. - Particle Size
Smaller SAP particles will have a faster rate of absorption as there is a greater surface area to attract aqueous liquid molecules. Larger SAP particles will absorb more slowly due to a lower available surface area to interact with aqueous liquids. - Situational circumstances
3.1 Ionic concentration of liquid e.g., the higher the salt content the lower the absorption
3.2 pH of the liquid – SAPs lose absorption capacity in low pH and high pH environments
3.3 Moderately higher temperatures will increase the rate of absorption.
3.4 Pressure – Absorption rate and capacity will be reduced when physical pressure is applied e.g., food pads with heavy steaks on top, or patients laying on dressings with a superabsorbent core.
COMMON SUPERABSORBENT APPLICATIONS
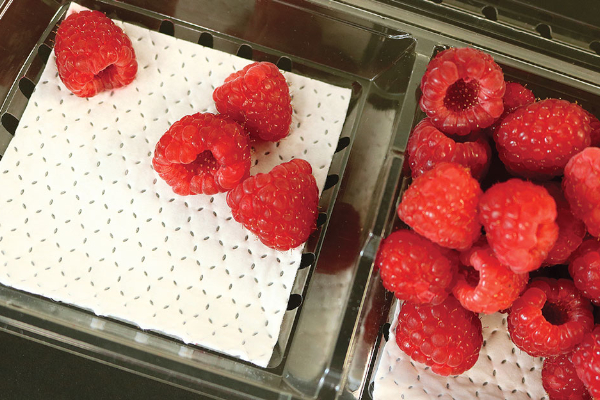

Meat and fruit pads
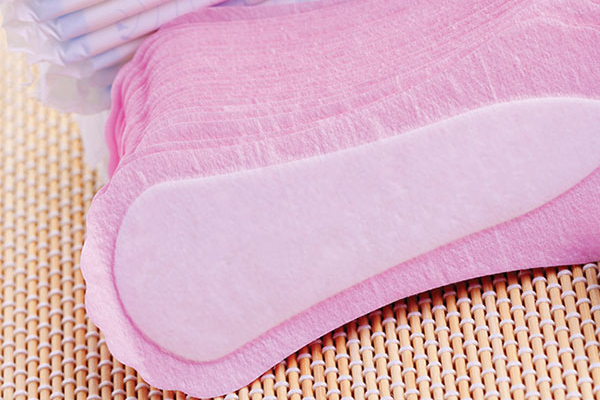

Personal absorbent hygiene products
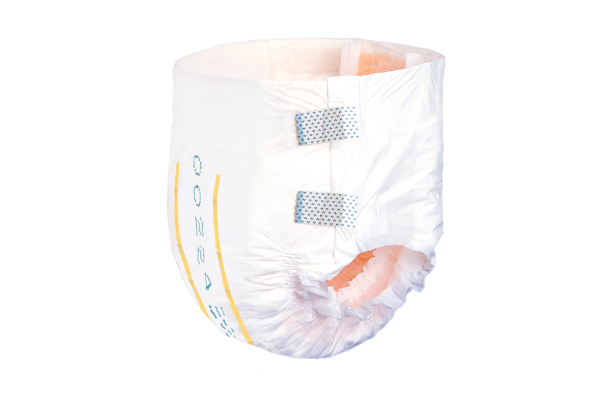

Baby diapers and disposable absorbent underwear
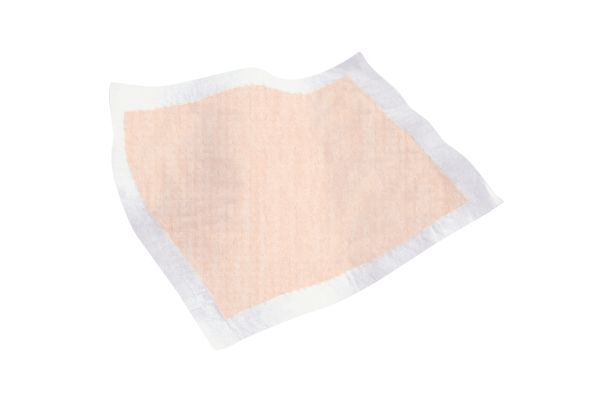

Incontinence pads
Wound care dressings
Biohazard absorption and protection
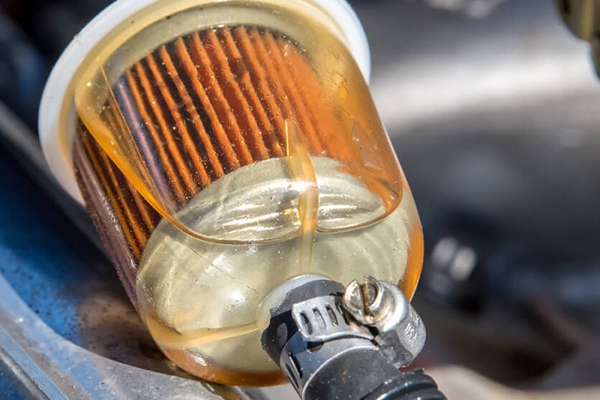

Fuel and oil dewatering
SAP Applications Include
- Meat and fruit pads
- Wound dressings
- Medical/surgical pads
- Fuel and Oil Filtration / Separation (Dewatering)Wire & cable water blocking
- Medical /surgical pads
- Industrial aqueous waste disposal
- Agriculture and horticulture uses e.g. seed coating or soil enhancement
- Artificial snow for movies and theaters
- Cement modifiers for civil engineering projects
- Flood sacks
- Ice packs
See the section called How SAP is changing the world to see more applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do superabsorbent polymers dissolve in water?
No, the cross-linked polymer chains form a gel with water and do not dissolve.
How are superabsorbent polymers used in agriculture?
The superabsorbent material, in the form of potassium polyacrylate, can be blended to enhance the performance of soil through water retention and slow release of a variety of nutrients and water soluble fertilizers. The potassium format is non toxic and hence preferred over sodium-based polymer to prevent salination of the soil which would be detrimental to plant health.
What is SAP used for
The most prevalent application is in personal absorbent hygiene products
Are superabsorbent polymers biodegradable?
Researchers are actively engaged in developing a solution to common SAP biodegradability, or SAP from renewable resources, as extremely large amounts of SAP are discarded into the environment every year.
Are superabsorbent polymers compostable?
Environmental impacts are a concern because the cross linked superabsorbent material does not easily degrade and it ends up in landfills on a large scale through baby diapers and other personal hygiene products.
Are superabsorbent polymers harmful?
The polymer itself is not an irritation to the skin, but irritation is possible if the manufacturing process results in some residual acrylic acid or monomer. Care should also be take to not inhale the dust or powder nor let the polymer come into contact with eyes.
Is superabsorbent polymer plastic?
Technically, sodium polyacrylate can be considered as a plastic as the polymer chains are derived from hydrocarbon sources
Can I flush superabsorbent polymer?
No. This is definitely not advised as these water absorbing materials will swell up and retain extremely large amounts of water and cause blockages in waste pipes and will contaminate sewerage treatment facilities.
Can superabsorbent polymer absorb oil?
No. This is not its intended use as it will only absorb aqueous based fluids
Can you eat superabsorbent polymer SAP?
Eating superabsorbent material is definitely not recommended as ingestion can lead to the polymer chains absorbing liquid and swelling up inside the body
Gelok’s Quality and Versatility in Superabsorbent Polymer Applications
Gelok extends its capabilities to produce specialized laminates tailored for water retention by utilizing various grades of tissue, polyester or airlaid substrates. These laminates incorporate a blend of superabsorbent materials and adhesive to optimize water absorption and retention properties.
All Gelok laminates and airlaid-style cores are manufactured in the form of bulk rolls, providing the flexibility to be slit into customer-specified widths or sheeted according to specific requirements. This adaptability ensures that Gelok products can be seamlessly integrated into diverse applications.
It’s worth noting that Gelok maintains high-quality standards in its manufacturing processes. The plant operates under a certified Quality Management System, as attested by Intertek, demonstrating conformity with ISO 9001:2015. This certification underscores Gelok’s commitment to delivering products that meet rigorous quality standards.
Contact us to learn more about Gelok’s superabsorbent polymers.
